Waste and Pollution Management
Management Approach and Relevant Policies
The Company is committed to managing waste and environmental pollution that may have an adverse impact on communities and the environment and drives business with sustainable development principles. The Company adopted the ISO14001:2015 environmental management system to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of its environmental management.
effectiveness of its environmental management. The Company aims to reduce upstream waste and invest in research to recycle waste or degraded raw materials for maximum benefit. Additionally, the Company focuses on managing and controlling environmental impacts in all aspects, such as water, air, and noise pollution, which may arise from its production, transportation, and various support processes in the business value chain. All activities are managed in compliance with legal requirements, stakeholder expectations, and established standards. The Company continuously plans its business development in alignment with environmental goals to achieve the objectives of the environment and sustainability policies
Target and Performance of Waste and Pollution Management

1. Waste management
The Company prioritizes minimizing waste and garbage generated from its production processes by adopting a 3Rs waste management approach: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. This approach aims to achieve the Zero Waste to Landfill goal. The waste management process includes segregation, storage, disposal, and documentation of waste, along with reporting to government agencies in compliance with legal requirements. The Company also promotes environmental awareness among employees by providing knowledge and understanding of waste disposal regulations and practices, as well as encouraging the reduction of production waste.
Types of waste and the management methods are as follows:
- Hazardous waste consists of waste or leftover materials that contain or are contaminated with hazardous substances or have dangerous properties as defined by the Ministry of Industry. This includes electrical and electronic equipment, containers and materials contaminated with oil or chemicals, oil, lubricants, and infectious waste from hospital rooms. These are managed by segregating and storing them in designated hazardous waste storage rooms with labeled indications. They are then disposed of by a hazardous waste disposal contractor authorized by a government agency through methods such as mixing with fuels, secure landfill, or incineration. Infectious waste is separated and securely bagged with tight closures. The Company has a contract with the hospital as a service provider to ensure proper disposal of infectious waste in compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Non-hazardous waste from the production process includes materials such as sludge, fat sludge, spoiled products, oil (cheese scraps, butter scraps, and flour scraps), raw materials, product packaging (metal buckets, plastic buckets, plastic, cling wrap, plastic bags), general office and cafeteria waste, food scraps, etc. The waste management method involves segregating these wastes into small groups before collecting and discarding them at designated points on a daily basis, according to the labeled indications to be sorted and used for recycling or repurposed into compost, soil conditioner, or animal feed. This waste can be disposed of by a waste disposal contractor authorized by the government agency through methods such as segregating waste for fuel production or sanitary landfills.
Performance on Waste and Pollution Management
In 2024, the total amount of waste and garbage was 3,175.5 tons, reflecting a 2.3% increase from 2023. This rise was attributed to the expansion of the butter and cheese production lines, the construction of KCG Logistics Park, and the renovation of Theparak Factory. However, over 99% of the waste consisted of garbage and non-hazardous waste.
The Company has reduced waste per ton of production from 87.37 kilograms to 81.09 kilograms per ton, representing a 7.2% decrease. Additionally, 83.7% of the total waste is recycled and reused.
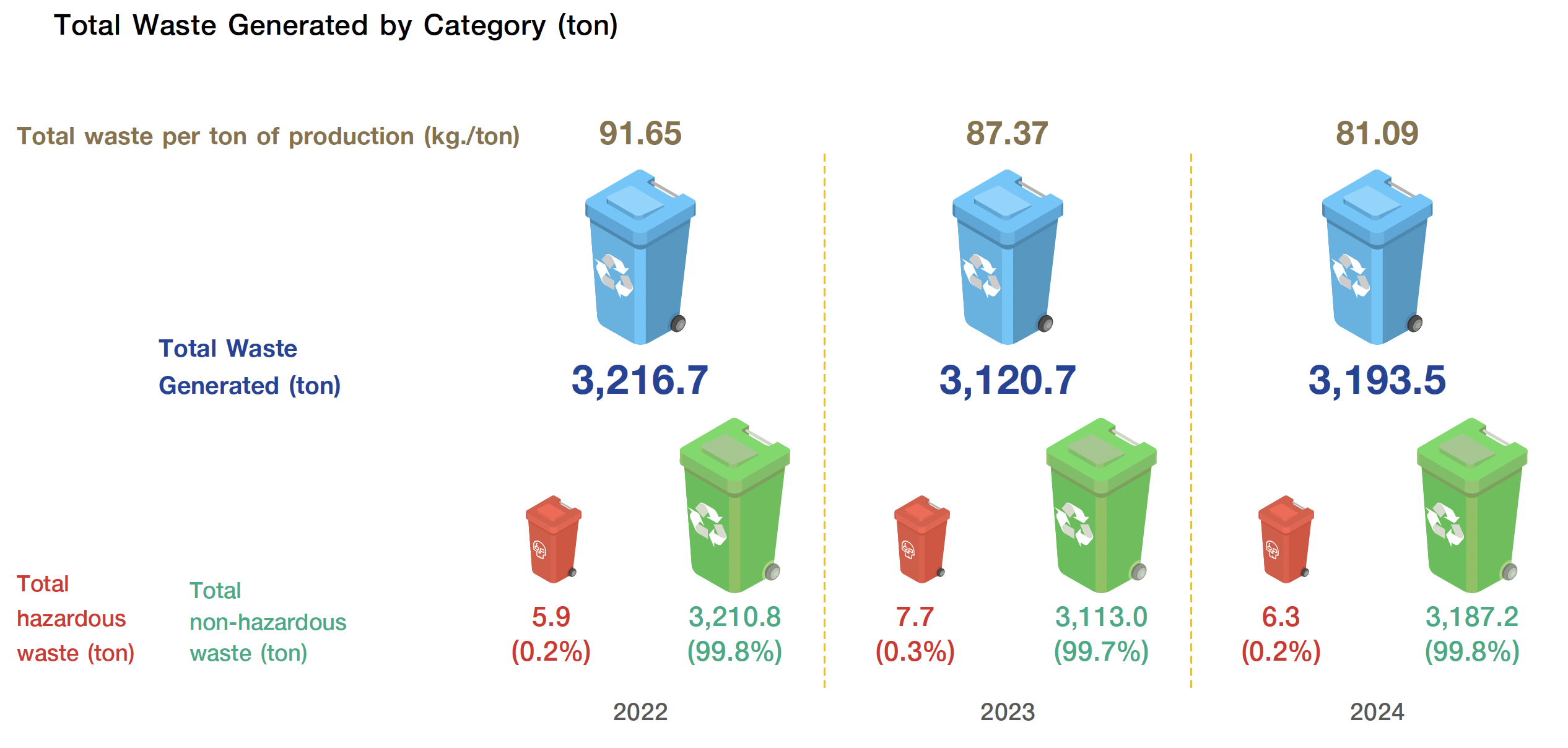
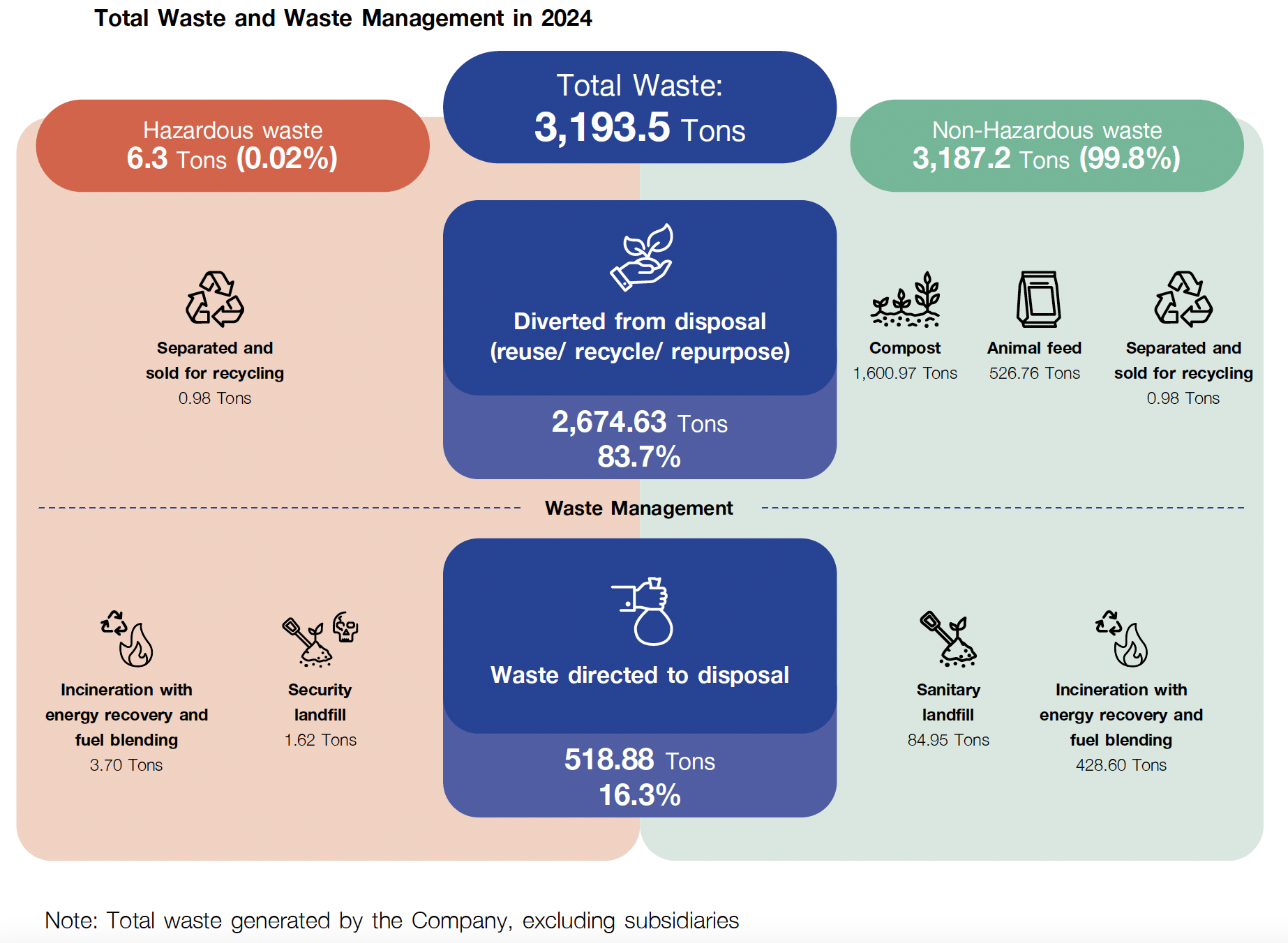
Total Waste Generated and Waste Management in 2024
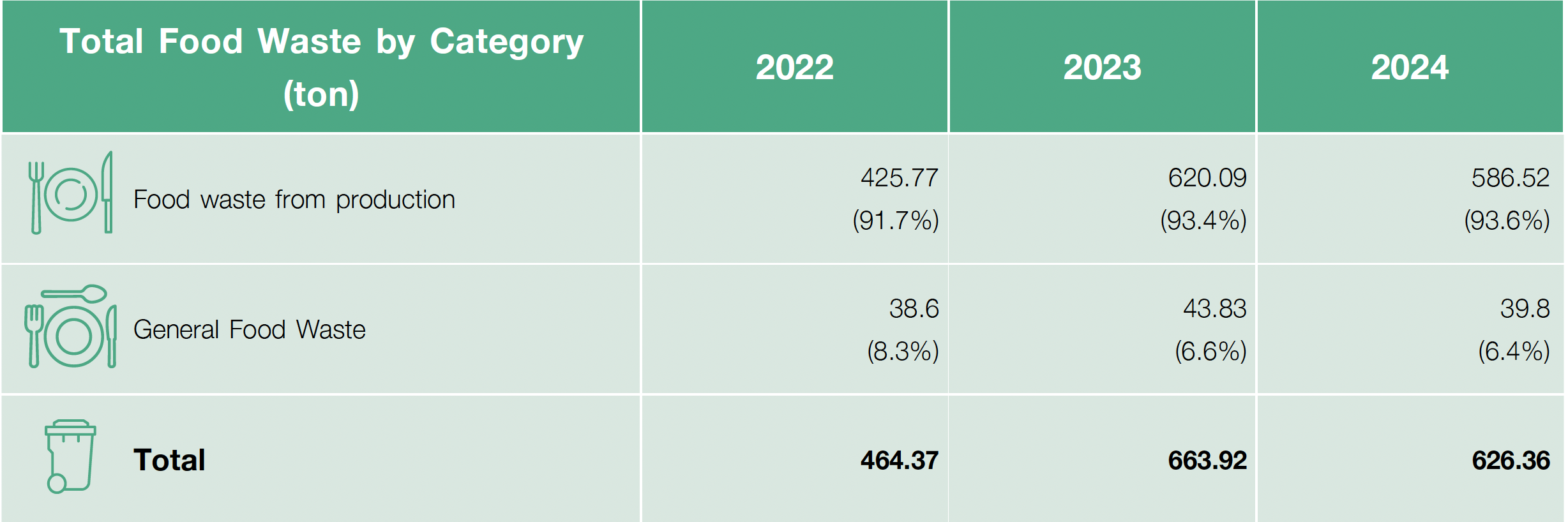
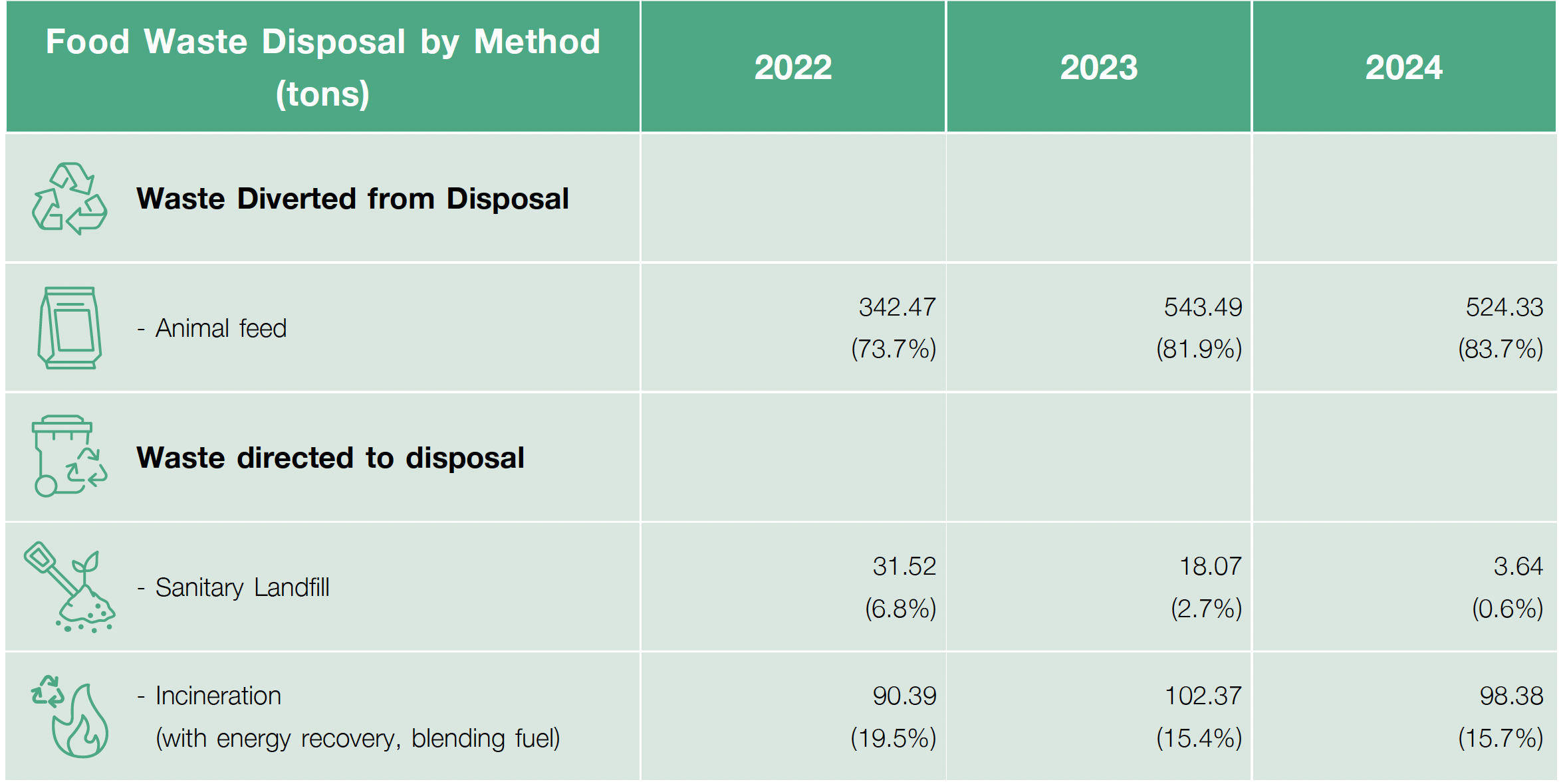
Food Waste Management
The Company established a food loss and food waste policy with a commitment to comply with food quality and safety standards to create sustainability in operations and reduce environmental impacts by reducing food loss and food waste in every step of the production and operations processes to increase efficiency and maximum benefit from raw materials used in food production in accordance with the Food Safety Certification System (FSSC 22000). The Company plans to reduce food loss and food waste by preventing food waste from the upstream stage, enhancing production efficiency, planning raw material purchases, managing inventory turnover to reduce expired products, and promoting awareness and consciousness among all employees and stakeholders.
For more information available in:
The Company’s food waste is categorized into two types and managed as follows:
- Food waste from production includes deteriorated products that can be reused, such as cheese scraps, butter scraps, and flour scraps. These are managed by segregating and selling them for further processing, such as turning them into fertilizer, components for agricultural planting materials, or raw materials for animal feed.
- General food waste from the office or cafeteria, such as food scraps, vegetables, and fruits, constitutes a smaller proportion compared to the waste from production. The Company separates this food waste at the cafeterias of both the Bang Phli Factory and Theparak Factory and disposes of it through the municipality for sanitary landfill.
Waste and Pollution Management
Zero Waste to Landfill Project
To achieve the goal of Zero Waste to Landfill 100%, the Company implemented a change in waste disposal methods at Theparak Factory at the end of 2022. The change was made from landfill disposal to incineration using a specially designed waste incinerator. This efficient waste disposal technique is capable of burning large amounts of nonrecyclable waste and includes a system to control gases and soot generated during combustion, preventing pollution and environmental disturbances. The result is that the heat energy from burning waste is utilized to produce steam or hot water for generating electricity and segregating waste for recycling. In 2024, Theparak Factory implemented Zero Waste to Landfill. The Company also has plans to expand the Zero Waste to Landfill project to the Bang Phli Factory and across the entire organization in the long term.
General Waste Reduction Project
The Company has initiated a change in environmental culture for factory workers by encouraging the segregation of plastic bottles, glass bottles, and beverage cans within the factory. This helps reduce the amount of general waste sent for incineration or landfill, and instead, it is directed into recycling management. Production line staff are guided to segregate plastic bags from packaging and raw materials preparation as well as other processes, ensuring that the plastic bags are free from contamination. Additionally, various types of waste are segregated into recyclable waste groups, which are then stored for sale to reduce the amount of general waste sent for incineration or landfill and contribute to recycling management efforts.


2. Air Pollution Management
The Company prioritizes air quality management in the workplace and surrounding communities, developing a plan to ensure air quality meets standard criteria and exploring ways to improve the system. The Company consistently improves air quality by establishing clear goals and regularly measuring and monitoring air quality to ensure regulatory compliance and stakeholder confidence. This includes implementing eco-friendly measures to ensure that air quality standards are met and continuously improving the Company’s air quality control systems.
Air Pollution Control
The Company has a Preventive Maintenance (PM) plan for hood systems installed in various locations, including the boiler. This includes monitoring and inspecting the laboratory’s fume hood systems, as well as the cheese pot and boiler once a year to ensure that they can properly filter the air before it is released outside the factory.
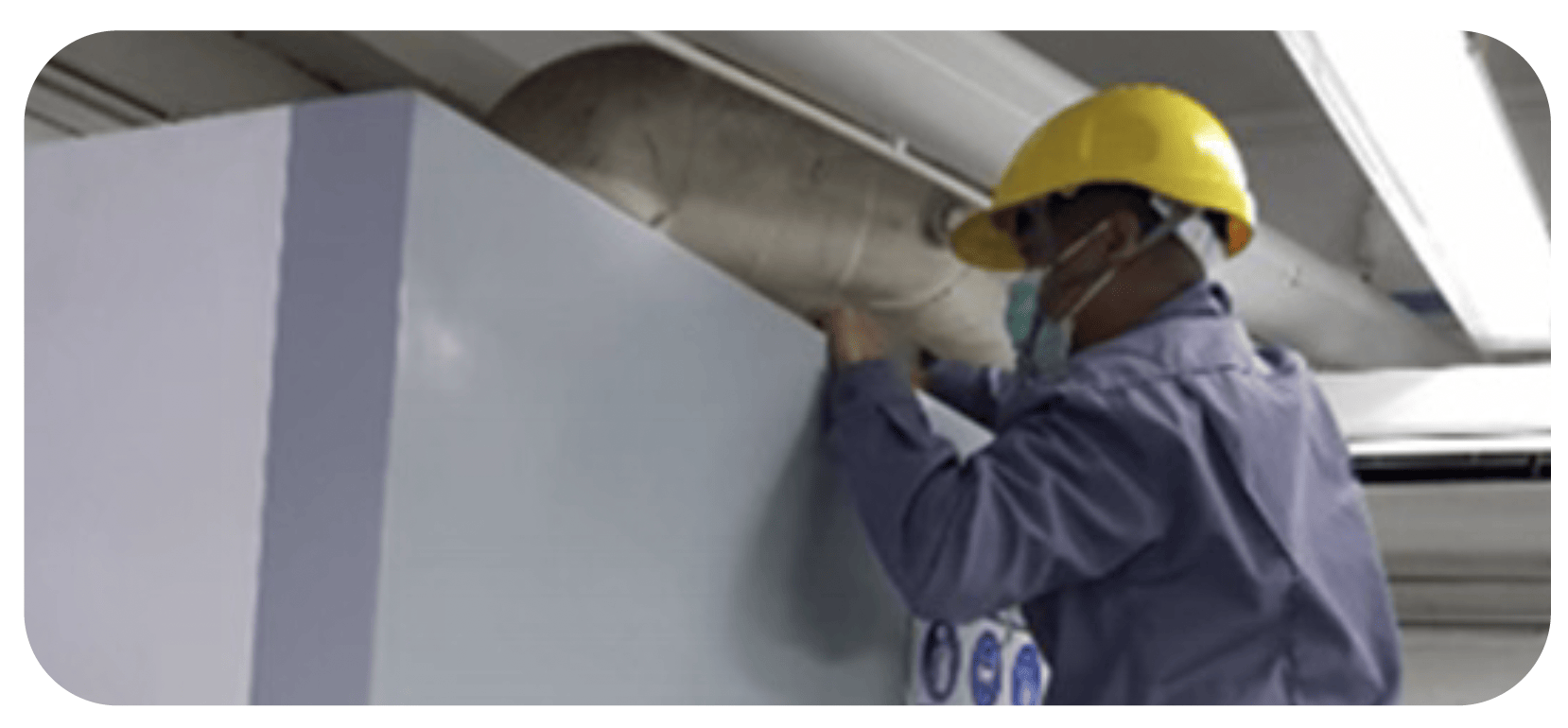

Air quality monitoring at the factory chimney tip
The Company conducts air quality monitoring parameters to check the released emissions at the tip of the factory’s chimney twice a year as required by law. A certified private analytical laboratory under ISO/IEC 17025 standards is hired to conduct air quality monitoring of factory emissions at the tip of the chimney in accordance with the Notification of the Ministry of Industry B.E. 2549 (2006) on the amount of chemical contaminants released from factories. The monitoring parameters include:
- Total Particulate Matter (TSP)
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx as NO2) The results of the air quality inspection at the chimney tip for 2023-2024 met all of the required parameters.
3. Environmental Complaints Management
The Company has established a systematic process for receiving and handling complaints in accordance with ISO14001:2015 standards, ensuring proper classification and appropriate management of each type of complaint. Various channels are available for stakeholders affected by environmental pollution to report issues directly, enabling the Company to take prompt corrective action. Additionally, the Company compiles and summarizes complaint resolutions for regular reporting and continuous improvement.
Key Performance
In 2024, the Company had no incidents of oil or chemical spills affecting the environment and surrounding communities. Additionally, there were no complaints regarding waste management or environmental pollution from surrounding communities or government agencies.
Sustainability Performance Data 2024 - Environmental Performance